New Delhi: India’s labour market showed sustained resilience in September, with the Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) climbing to a five-month high of 55.3%, marking the third consecutive month of improvement, according to the latest Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) released by the National Statistical Office (NSO) of the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
The data highlights continued recovery in labour market engagement, particularly among women, even as the unemployment rate edged up marginally.
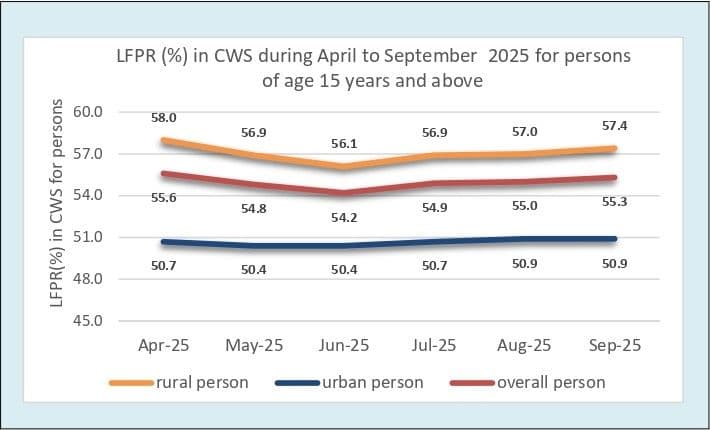
The LFPR — which measures the share of people aged 15 years and above who are either employed or actively seeking work — rose from 54.2% in June to 55.3% in September, indicating a broader revival in work participation. The rise was driven largely by the rural workforce, where participation increased from 56.1% in June to 57.4% in September. Urban LFPR, meanwhile, held steady at 50.9%.
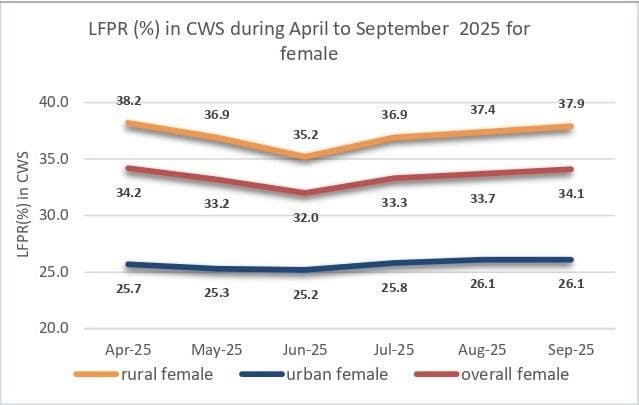
Female participation remained a bright spot, underscoring a positive shift in workforce dynamics. The female LFPR climbed to 34.1%, the highest since May 2025, supported by steady gains in rural areas where it rose from 35.2% in June to 37.9% in September. Analysts say this continued upward trend suggests gradual but encouraging improvements in female employment opportunities, particularly in agriculture, manufacturing, and services linked to rural infrastructure and social programmes.
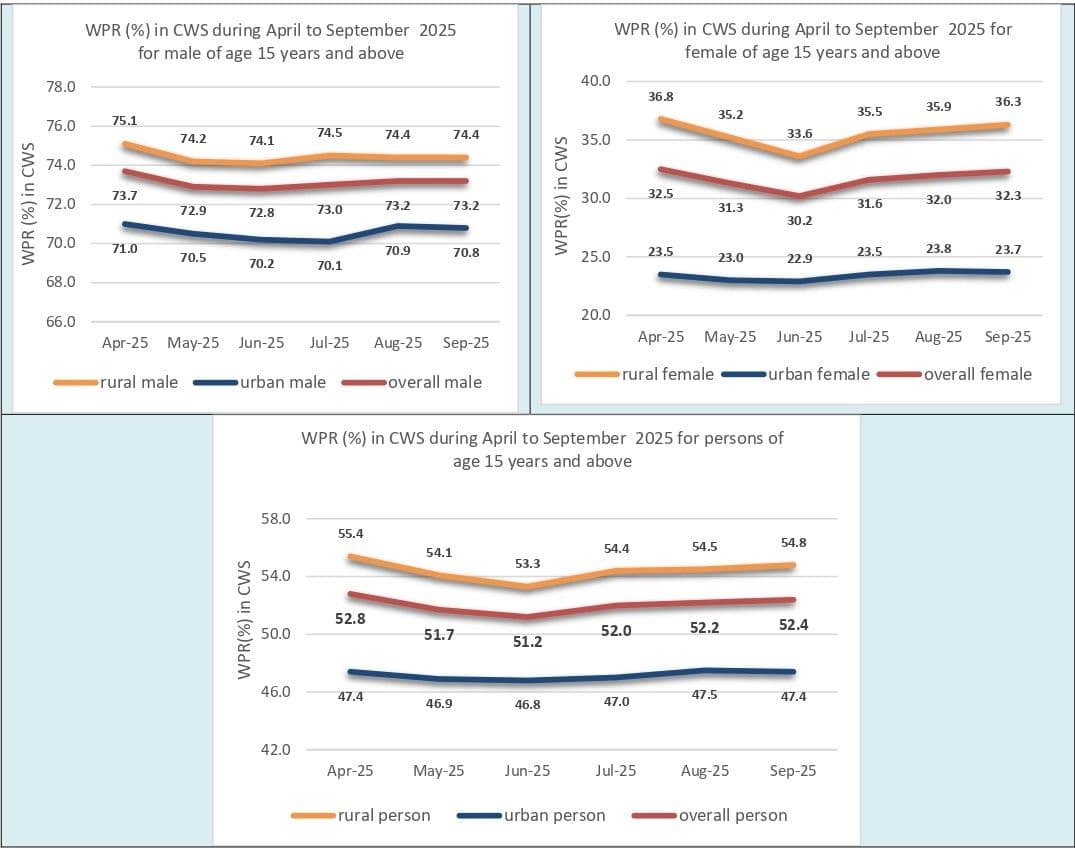
The Worker Population Ratio (WPR), which measures the proportion of employed persons among the population aged 15 years and above, also improved to 52.4% — the highest since May 2025. The WPR for women increased for the third straight month, indicating not just more women entering the labour force but also more of them finding work.
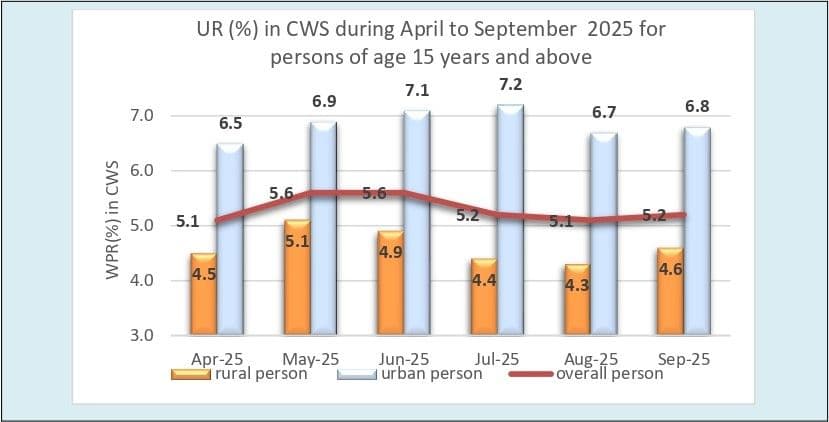
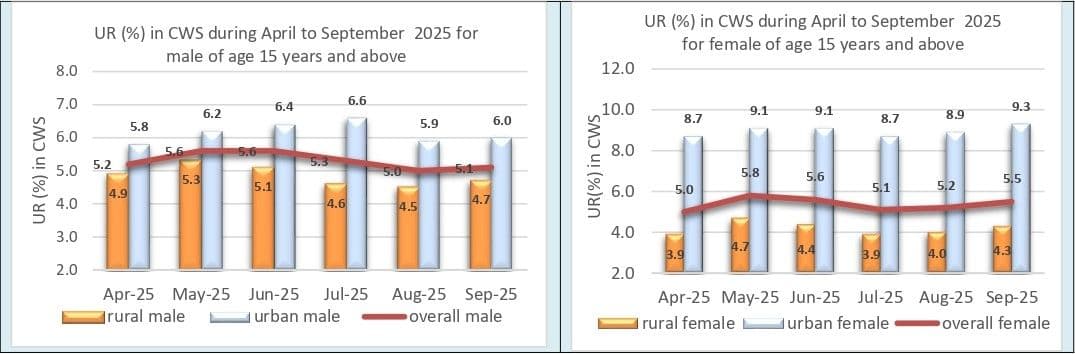
However, the data showed a slight uptick in the Unemployment Rate (UR), which rose to 5.2% in September from 5.1% in August, ending a two-month decline. The increase was modest and largely attributed to higher joblessness in rural areas, where UR climbed from 4.3% to 4.6%, while in urban areas it edged up from 6.7% to 6.8%.
Female unemployment also reflected this pressure. The overall female UR rose from 5.2% in August to 5.5% in September, with urban female unemployment increasing more sharply from 8.9% to 9.3%. For men, unemployment increased marginally across both rural and urban areas to 4.7% and 6.0%, respectively.
Economists note that the simultaneous rise in participation and mild uptick in unemployment reflects a healthy labour market adjustment, where more individuals — especially women — are actively seeking work. “A modest rise in unemployment rate alongside higher participation often signals improving job-seeking sentiment rather than economic weakness,” said a senior labour economist.
The September bulletin is the sixth in the new monthly PLFS series, introduced earlier this year after a methodological revision to provide higher-frequency estimates of key employment indicators. The latest round covered a total of 3.75 lakh individuals across India, including 2.15 lakh in rural areas and 1.6 lakh in urban centres, under the Current Weekly Status (CWS) approach.
With both LFPR and WPR at multi-month highs, policymakers see the data as a positive indicator of expanding labour market engagement amid a gradually stabilizing economic environment. The sustained improvement in female participation, in particular, could contribute significantly to long-term productivity and inclusive growth.
While the marginal rise in unemployment calls for continued policy focus on job creation — especially in urban sectors — the overall momentum suggests India’s labour market is showing broad-based resilience heading into the second half of FY26.